NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 – Human Reproduction

Q1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Humans reproduce _____ (asexually/sexually)
(b) Humans are _____ (oviparous, viviparous, ovoviviparous)
(c) Fertilisation is _____ in humans (external/internal)
(d) Male and female gametes are _____ (diploid/haploid)
(e) Zygote is _____ (diploid/haploid)
(f) The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called _____
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called _____
(h) The fusion of male and female gametes is called ____
(i) Fertilisation takes place in _____
(j) Zygote divides to form _____ is implanted in uterus.
(k) The structure which provides vascular connection between foetus and uterus is called _____
(a) Humans reproduce sexually.
(b) Humans are viviparous.
(c) Fertilisation is internal in humans.
(d) Male and female gametes are haploid.
(e) Zygote is diploid.
(f) The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called ovulation.
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called luteinising hormone (LH).
(h) The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation.
(i) Fertilisation takes place in the ampullary region of the fallopian tube.
(j) Zygote divides to form blastocyst which is implanted in the uterus.
Q2. Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
Diagrammatic representation of male reproductive system:
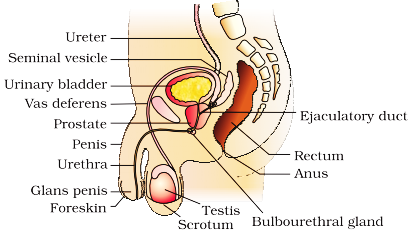
It consist of Testis, scrotum, epididymis, Vas deferens or sperm duct, seminal vesicles, prostrate gland, penis.
Q4. Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system.
Diagrammatic representation of female reproductive system:
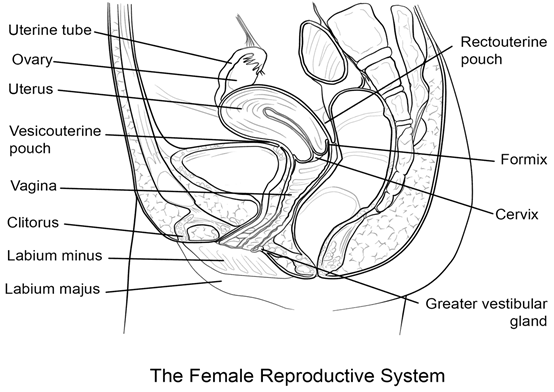
The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries along with a pair of oviducts, uterus, cervix, vagina and the external genitalia located in pelvic region.
Q4. Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Functions of Testis:
- Production of sperm through the process called spermatogenesis.
- Synthesis and secretion of testicular hormones called androgens by Leydig cells.
Functions of Ovary:
- Production of female gamete (ovum) through a process called oogenesis.
- Secretion of several steroid hormones, collectively known as ovarian hormones.
Q5. Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
The seminiferous tubule is a highly coiled structure found in the testis. Each seminiferous tubule is lined on its inside by two types of cells: male germ cells (spermatogonia) and Sertoli cells. The male germ cells undergo meiotic divisions to produce sperm, while Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the germ cells. Outside the seminiferous tubules, the interstitial spaces contain Leydig cells that secrete androgens, and small blood vessels are also present. Seminiferous tubules are essential for the process of spermatogenesis.
Q6. What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Spermatogenesis is the process by which sperms are produced in the male's testis. It begins at puberty due to increased secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the secretion of luteinising hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
Process of Spermatogenesis :–
- Spermatogonia Proliferation: Immature male germ cells, spermatogonia, multiply through mitosis and increase in number, remaining diploid with 46 chromosomes.
- Formation of Primary Spermatocytes: Some spermatogonia become primary spermatocytes and undergo meiosis.
- Meiotic Division: The first meiotic division produces two haploid secondary spermatocytes, each with 23 chromosomes.
- Transformation to Spermatids: Secondary spermatocytes undergo a second meiotic division, forming four haploid spermatids.
- Spermiogenesis: Spermatids transform into mature spermatozoa (sperms).
- Spermiation: Sperm heads embed in Sertoli cells of seminiferous tubules and are eventually released.
The entire process is regulated by hormones such as LH and FSH acting on Leydig and Sertoli cells, respectively.
Q7. Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
The hormones involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis are:
- Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) - Secreted by the hypothalamus, it stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release gonadotropins.
- Luteinising Hormone (LH) - This hormone acts on Leydig cells to stimulate the synthesis and secretion of androgens.
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) - It acts on Sertoli cells and stimulates some factors that aid in spermiogenesis.
Q8. Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.
- Spermiogenesis is the process where spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperms).
- Spermiation is the process after spermiogenesis where sperm heads become embedded in the Sertoli cells and are finally released from the seminiferous tubules.
Q10. What are the major components of seminal plasma?
The major components of seminal plasma are:
- Fructose
- Calcium
- Certain enzymes
Q11. What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
The major functions of male accessory ducts are to store and transport sperms from the testis to the outside through the urethra. The ducts include the rete testis, vasa efferentia, epididymis, and vas deferens. As for the male accessory glands, they include the seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands. The secretions from these glands contribute to the seminal plasma, which is rich in fructose, calcium, and enzymes, aiding in sperm nutrition and motility. The secretion of the bulbourethral glands also helps in lubricating the penis.
Q12. What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis.
Oogenesis is the process of formation of a mature female gamete. It begins during the embryonic development stage, where millions of oogonia are formed in the fetal ovaries. These oogonia start dividing and enter into prophase-I of meiotic division, becoming primary oocytes. Each primary oocyte is surrounded by granulosa cells, forming the primary follicle. By puberty, many of these follicles degenerate, leaving around 60,000–80,000 primary follicles per ovary. The primary follicles mature into secondary follicles, then transform into tertiary follicles with an antrum. The tertiary follicle continues to undergo changes to become a mature Graafian follicle. The primary oocyte completes its first meiotic division, resulting in a secondary oocyte and a small polar body. Finally, this mature follicle releases the ovum through a process known as ovulation.
Q13. Name the functions of the following: Corpus luteum
The corpus luteum has the following functions:
- The corpus luteum secretes large amounts of progesterone, which is essential for the maintenance of the endometrium.
- A well-maintained endometrium is necessary for the implantation of a fertilized ovum and other events of pregnancy.
Q14. Name the functions of the following: Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner glandular layer of the uterus and it plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle. It undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle and is essential for implantation of the fertilized ovum and maintenance of pregnancy.
Q15. Name the functions of the following: Acrosome
The acrosome is a cap-like structure that covers the anterior portion of the sperm head. It is filled with enzymes that assist in the fertilisation of the ovum.
Q16. Name the functions of the following: Sperm tail
The function of the sperm tail is to facilitate sperm motility essential for fertilisation.
Q17. Name the functions of the following: Fimbriae
Fimbriae are finger-like projections located at the edge of the infundibulum, which is part of the oviduct (fallopian tube). They play a critical role in the female reproductive system by helping in the collection of the ovum after ovulation.
16. Identify True/False statements. Correct each false statement to make it true.
a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells. (True/False)
b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells. (True/False
c) Leydig cells are found in ovary. (True/False)
d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens. (True/False)
e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. (True/False)
f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. (True/False)
g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience. (True/False)
a) False: Androgens are produced by Leydig cells, not Sertoli cells.
b) True: Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells.
c) False: Leydig cells are found in the testes, not the ovary.
d) True: Leydig cells synthesize androgens.
e) False: Oogenesis takes place in the ovaries, not in the corpus luteum.
f) True: Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy.
g) True: Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience.
Q17. What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle is the reproductive cycle in female primates, including humans, and it starts with the first menstruation at puberty, called menarche. It is repeated at an average interval of approximately 28/29 days. The key events involve the menstrual phase, follicular phase, ovulatory phase, and luteal phase. Hormones regulating the menstrual cycle include:
- Gonadotropins (LH and FSH)
- Estrogens
- Progesterone
The secretion of LH and FSH increases during the follicular phase, stimulating follicular development and secretion of estrogens. LH surge leads to ovulation, while progesterone from the corpus luteum maintains the endometrium.
18. What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
- Parturition is the process of delivery of the foetus (childbirth).
- It is induced by a complex neuroendocrine mechanism.
- The hormones involved in the induction of parturition are oxytocin from the maternal pituitary and signals from the fully developed foetus and placenta.
- These signals trigger mild uterine contractions called the foetal ejection reflex, leading to stronger contractions and secretion of oxytocin, which aids in expelling the baby.
19. In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
The sex of the baby is determined at the stage of fertilization and is decided by the sperm from the father. Male gametes (sperms) carry either an X or a Y chromosome, whereas female gametes (ova) only carry an X chromosome. When a sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the ovum, it results in a female child (XX), and when a sperm containing a Y chromosome fertilizes the ovum, it results in a male child (XY). Therefore, it is scientifically accurate to state that the sex of the child is determined by the father's contribution and not by the mother.
20. How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal?
- A human ovary typically releases one egg per month.
- If the mother gave birth to identical twins, only one egg would have been released as identical twins result from the splitting of a single fertilized egg.
- If the twins were fraternal, two eggs would have been released, as fraternal twins come from two separate eggs being fertilized by two separate sperm cells.
Q21. How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Dogs and rodents are polyovulatory species i. e. produces more than one egg at a single time. Dogs can give birth to multiple puppies because they have the potential to release multiple eggs during a reproductive cycle. However, the exact number of eggs released can vary widely depending on the breed and individual dog. Generally, the number of eggs released corresponds to the number of puppies born, so if a dog has 6 puppies, it is likely that around 6 eggs were released, although some eggs may not result in a viable pregnancy. Identical twins in dogs are rare, while fraternal twins are more common due to the release of multiple eggs.

