Summary + MCQS – Class 6 Science Chapter 3 (Fibre to Fabrics)
Watch Video Lecture Here ..
Video Lecture: Fibre to Fabric
Fibres are the materials, which are available in the form of thin, continuous and flexible strands spun into yarn and made into fabrics.
Fabrics are defined as a cloth material made by knitting or weaving or of threads together.
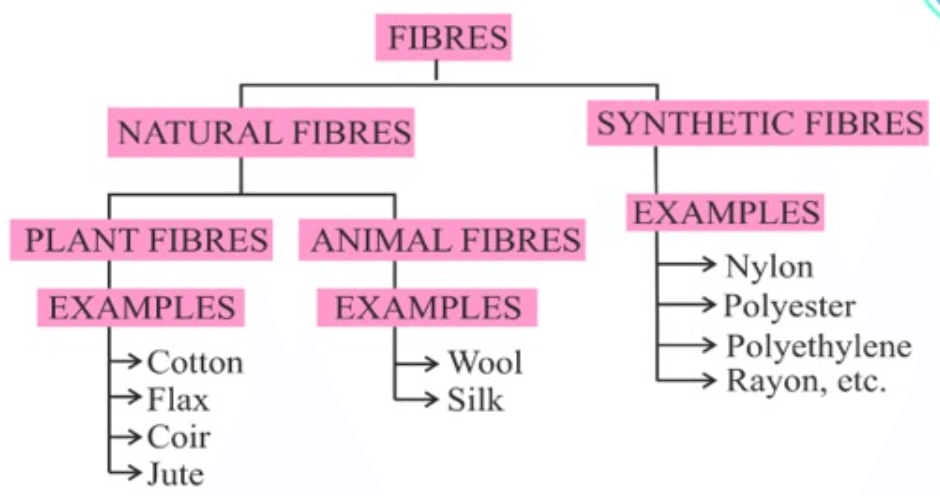
Types of Fibre
There are two types of fibres classified according to their origin.
- Natural fibres: These fibres are naturally obtained from plants and animals. Cotton and jute are fibre obtained from plants. Silk and wool are fibre obtained from animals.
- Synthetic fibres: These fibres are artificially synthesized by humans within the industry by the application of simple chemicals. Examples: Acrylic, polyester, nylon, rayon, acetate, are a few examples of Synthetic fibre.
Variety of Natural Fibre
Natural fibres are obtained from two sources. They are Plant fibre and Animal fibre.
Plant fibre
The fibre which are obtained from plant are known as Plant fibre.
Examples: Cotton, Jute etc.
Cotton
- The plants of cotton are usually grown at the places having black soil and warm climate.
- Cotton grows in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Odisha etc.
- The fruit of cotton is known as cotton bolls.
- From the bolls, cotton is usually picked by hand.
- Ginning is the process of separating cotton fibres from the seeds by combing. It was traditionally done by hands, now machines are available for ginning.
Ginning
- The plant from which cotton is picked contains seeds. The process of removing these seeds from cotton pods is known as ginning.
- Ginning can be done using hands or by machines.
Spinning
- The process of making yarn from thin strands of fibres is called spinning.
- It can be done by hand or on a spinning wheel.
Spinning cotton yarn
- Fabrics are made from yarns, which in turn are made from fibres.
- The process of making yarn from raw fibrous materials is called spinning. In this process, the fibres are twisted to make yarn.
- Making fabric from yarn is done by two processes:
- Weaving : It is a process in which the two sets of yarn arranged together to make a fabric is called weaving. It is done by looms.
- Knitting :The process by which a single yarn is used to make fabric. It is done by hand or by help of machines.
Jute
- Jute is used for making of bags and ropes mats etc.
- Jute fibre is obtained from stem of the jute plant.
- The cultivation of jute is in rainy season.
- The cultivation of jute is in west Bengal, Bihar and Assam.
- When the jute plant is in flowering stage the harvesting is take place.
- The stems of the jute plant are immersed in water for a few days which then rot and fires are separated by hand and this process is called stripping.
- Then the stripped fibres are washed and dried in sun
Animal Fibres
- Silk and wool are fibre obtained from animals.
- Wool fibres come from sheep, camel, goat, and yak.
- The process involved in making animal fibres into wool follows a series of steps — Shearing, Scouring, Sorting, Cleaning, Dyeing, Straightening, Rolling and Combing.
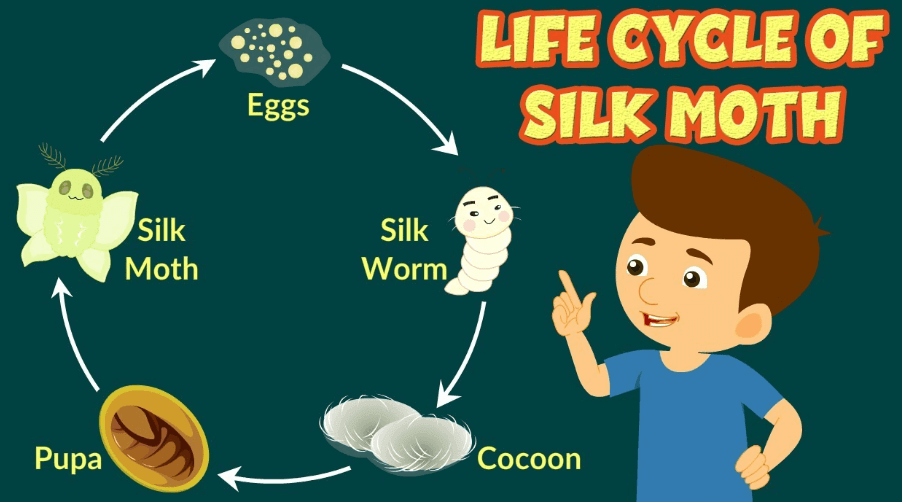
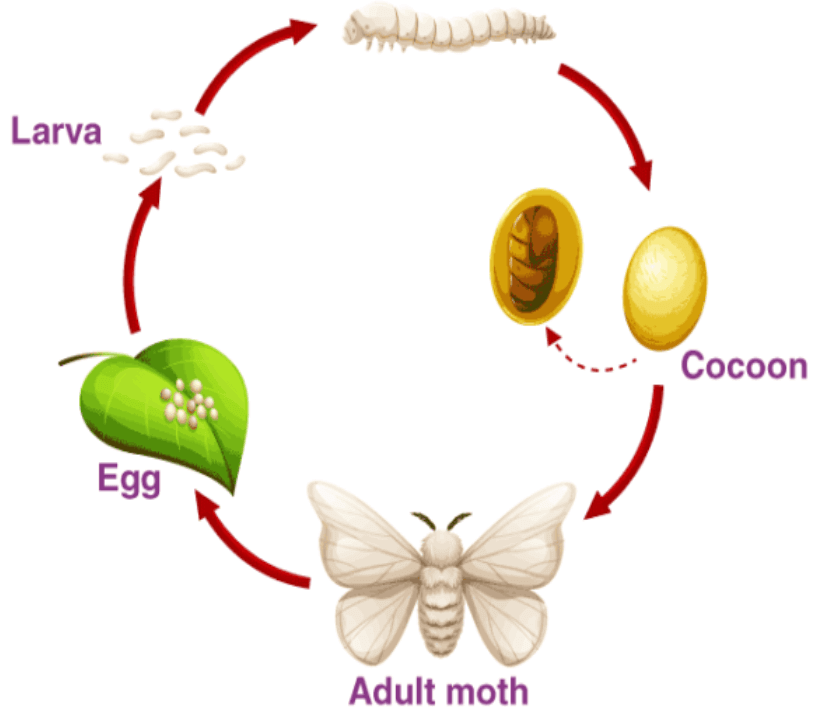
- Silk fibres are obtained from the silkworm and the process of obtaining silk from the silkworm is called sericulture. The silk thread or the yarn is obtained from the silk moth’s cocoon.
The life cycle of a silkworm begins from the:
Stage 1 - After mating, female silk moth lays around 200 – 300 eggs at a time.
Stage 2 - The egg hatches and new silkworms arise and feed on mulberry leaves for around 30 days and move into the next stage.
Stage 3 - Cocoon, a protective layer or a silky web spun is developed around the larvae, which is the size of a small cotton ball made of a single silk thread.
Stage 4 - Pupa stage. A stage where silk fibres is obtained by killing the pupa and plunging the cocoon into boiling water and unwind the silk thread.
Stage 5 - The last stage of a life cycle, in which the completely developed pupa changes into an adult moth. Again the life cycle begins from here.
History of clothing material
Ancient people used the bark and big leaves of tree or animals skins or furs to cover themselves.
After settling in agriculture communities, they learnt to weave twigs and grass into mats and baskets. Early Indians wore fabrics made out of cotton.
In ancient Egypt, cotton as well as flax was used for making fabrics. After the invention of the sewing needle, people started stitching fabrics to make cloth.

